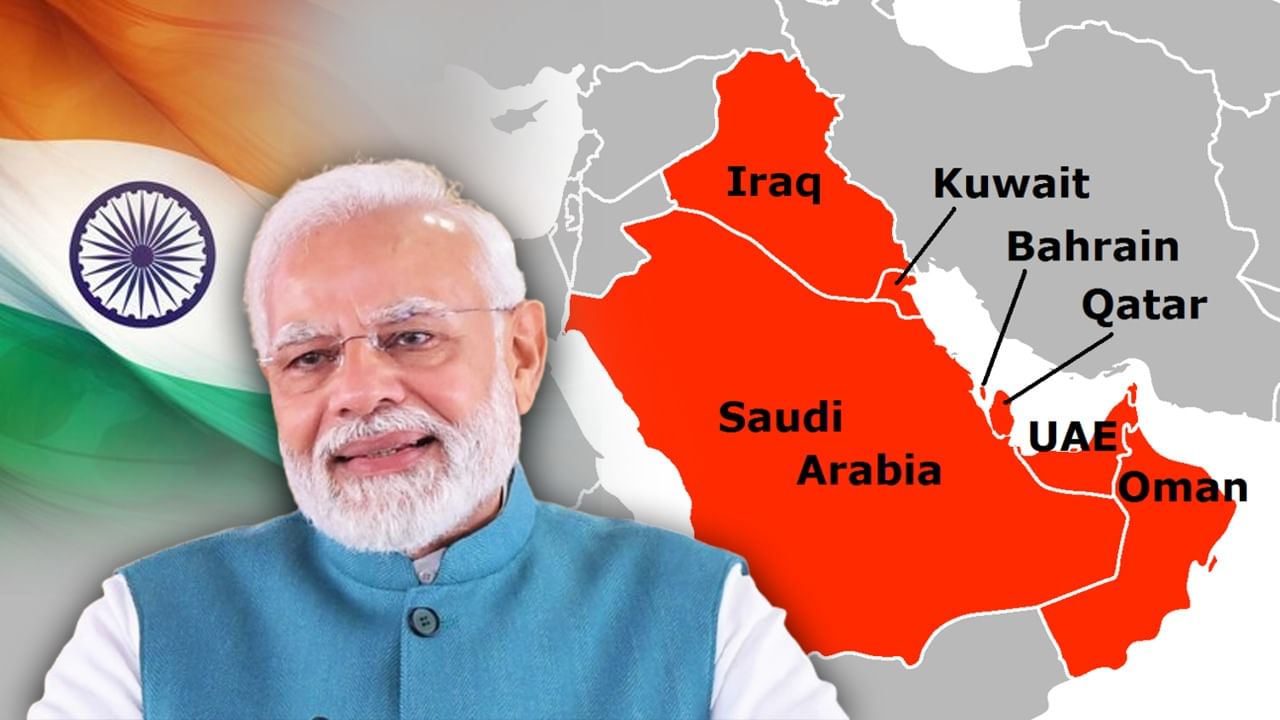
A recent defense agreement between Saudi Arabia and Pakistan has ignited a new discussion regarding India’s relations with the Gulf countries. This agreement stipulates that an attack on one country will be considered an attack on the other, potentially including the use of Pakistan’s nuclear weapons. While Pakistan’s Defense Minister clarified that Saudi Arabia would not receive nuclear protection under the deal, the agreement has sparked questions about India’s most reliable and steadfast allies in the region. The Gulf nations, comprising Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Iraq, Bahrain, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Oman, share borders with the Arabian Gulf (Persian Gulf). India’s historical, cultural, energy, and trade ties with these countries are long-standing, with a significant Indian diaspora residing there. Saudi Arabia stands as a traditional partner for India, with deepening relations across energy, trade, investment, and security over the past two decades. The current presence of approximately 2.6 million Indians in Saudi Arabia strengthens this bond. The UAE is perhaps India’s most significant partner, with nearly 4.3 million Indians, representing about 35% of the total population. Trade between India and the UAE reached $28.4 billion in 2021-22, with projections estimating it could reach $100 billion by 2026. The UAE also accounts for approximately 27% of India’s total remittances. Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Oman also have significant Indian populations and strong relationships with India, contributing to their economic and social development. Iraq is vital for India’s oil needs, importing 22% of its total crude oil from Iraq. India’s relationship with the Gulf nations rests on three pillars: the Indian diaspora, remittances, and energy and trade. With nearly 8.9 million Indians in the Gulf countries, India receives the world’s highest remittances annually, with over half originating from these nations. Furthermore, India fulfills 60% of its oil needs and conducts $154 billion in trade with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC). In return, India supplies 85% of the food and grain needs of the Gulf countries, including rice, spices, seafood, and meat. Indian travelers also represent a large customer base for Gulf airlines. While the new defense agreement between Saudi Arabia and Pakistan is a concern for India, India’s relations with the Gulf countries are deeply rooted and multifaceted. While Saudi Arabia is crucial for energy and political cooperation, the UAE is India’s closest partner in terms of expatriates and trade. Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, and Oman are also reliable friends because of their significant Indian communities and economic collaboration. The UAE and Saudi Arabia appear to be the leading allies.
Subscribe to Updates
Get the latest creative news from FooBar about art, design and business.